Rosacea vs Acne: Key Differences and How to Treat Them
Rosacea and acne can look alike but require very different treatments. Learn how to identify key differences, manage triggers, and treat each condition effectively.

Introduction
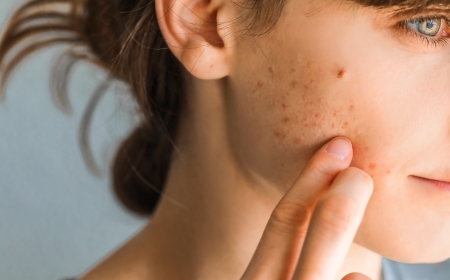
At first glance, rosacea and acne may appear similar both involve facial bumps, redness, and irritation. But they are two different skin conditions with unique causes and treatments.
Misdiagnosing one for the other can make things worse. For example, acne products might irritate rosacea-prone skin, leading to rosacea flare-ups. Thats why its essential to understand the key differences between rosacea and acne, so you can treat your skin the right way.
2. What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic skin redness condition that mainly affects the central face. It tends to develop gradually and can get worse over time if left untreated.
Types of Rosacea:
-
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea: Persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, and flushing
-
Papulopustular rosacea: Red bumps and pus-filled pimples, often mistaken for acne
-
Phymatous rosacea: Thickened skin and enlarged pores (typically around the nose)
-
Ocular rosacea: Affects the eyes with redness, dryness, and irritation
Common Symptoms of Rosacea:
-
Flushing or blushing easily
-
Redness across the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin
-
Visible broken blood vessels
-
Burning or stinging sensation
-
Bumps that resemble acne but lack blackheads
Rosacea Triggers:
-
Spicy foods
-
Alcohol
-
Hot weather or sudden temperature changes
-
Stress
-
Skincare products with harsh ingredients
Recognizing and avoiding rosacea triggers is a key part of any rosacea skincare routine.
3. What Is Acne?
Acne is caused by clogged pores due to excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Its more common in teenagers but can occur at any age.
Types of Acne:
-
Blackheads and whiteheads
-
Papules and pustules
-
Nodules and cystic acne (deep and painful)
Common Acne Areas:
-
Face (especially the T-zone)
-
Back
-
Chest
-
Shoulders
While acne also causes redness and inflammation, it is fundamentally different from the rosacea skin condition in both cause and treatment.
4. Key Differences Between Rosacea and Acne
Understanding how rosacea and acne differ helps in choosing the right approach:
|
Aspect |
Rosacea |
Acne |
|
Age of Onset |
30+ years |
Teens to early 20s |
|
Location |
Central face (cheeks, nose) |
Face, back, chest |
|
Redness |
Common and persistent |
Temporary with pimples |
|
Blackheads |
Rare |
Common |
|
Flare-ups |
Triggered by lifestyle or environment |
Linked to hormones, bacteria |
|
Skin Texture |
Often dry/sensitive |
Often oily |
Also, sensitive skin rosacea may react poorly to acne treatments, which are typically stronger and more drying.
5. How to Diagnose: When to See a Dermatologist
If youre unsure whether you have acne or rosacea, consult a dermatologist for rosacea or acne. A skin specialist can:
-
Examine your skins pattern and reaction to triggers
-
Ask about your history of blushing, redness, or breakouts
-
Use diagnostic tools like dermoscopy or skin biopsy (if needed)
Getting a proper diagnosis is the first step toward effective rosacea treatment or acne management.
6. Treatment Options for Rosacea
There is no cure for rosacea, but it can be managed with the right approach:
? Topical Treatments:
-
Metronidazole and azelaic acid are anti-inflammatory and reduce redness
-
Prescription anti-redness creams can target visible blood vessels
? Oral Medications:
-
Antibiotics like doxycycline for moderate to severe papulopustular rosacea
? Laser Treatment for Rosacea:
-
Targets visible veins and persistent redness
-
Often used for erythematotelangiectatic rosacea
? Lifestyle & Skincare Changes:
-
Identify and avoid rosacea triggers
-
Use gentle cleansers and avoid alcohol-based products
-
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily
If you prefer rosacea natural treatment options, soothing agents like green tea, niacinamide, or aloe vera may help reduce irritation.
7. Treatment Options for Acne
Acne is usually more responsive to over-the-counter and prescription treatments:
? Topical Products:
-
Benzoyl peroxide (kills bacteria)
-
Salicylic acid (clears pores)
-
Retinoids (prevent new breakouts)
? Oral Medications:
-
Antibiotics, birth control pills, or isotretinoin in severe cases
? Skincare & Lifestyle:
-
Cleanse skin twice daily with a mild cleanser
-
Avoid heavy oils or comedogenic makeup
-
Maintain a balanced diet and reduce sugar intake
The best approach is consistent care using products suited to your skin type.
8. Can You Have Both Rosacea and Acne?
Yes, its possible to have both. Some people with rosacea on cheeks and nose may also experience oily skin and acne on other areas.
In these cases, treatments must be balancedstrong acne medications can worsen rosacea, while rosacea products might not clear acne.
Dermatologists often recommend a customized routine with products that are:
-
Non-comedogenic
-
Fragrance-free
-
Designed for sensitive skin with rosacea
9. Preventing Flare-Ups and Breakouts
Whether you have rosacea, acne, or both, prevention is key:
-
Follow a gentle rosacea skincare routine with minimal products
-
Apply sunscreen daily (SPF 30 or higher)
-
Avoid hot showers, spicy food, and alcohol
-
Use lukewarm water for cleansing
-
Choose makeup labeled for sensitive or rosacea-prone skin
Even the best cream for rosacea won't help if you continue using irritating products or skipping sunscreen.
Although rosacea and acne may look similar, they are fundamentally different conditions with unique causes and treatments. Rosacea is characterized by persistent redness and sensitivity, while acne involves clogged pores and inflammation.
Understanding the differences in symptoms, triggers, and treatment is essential for healthy skin. If you're dealing with chronic facial redness or recurring breakouts, its best to consult a professional.
Takeaway:
Dont self-diagnose what looks like acne might be rosacea, and treating it incorrectly can make it worse. For best results, work with a dermatologist for rosacea to develop a treatment plan tailored to your skin.